How did Greek culture influence Hadrian?
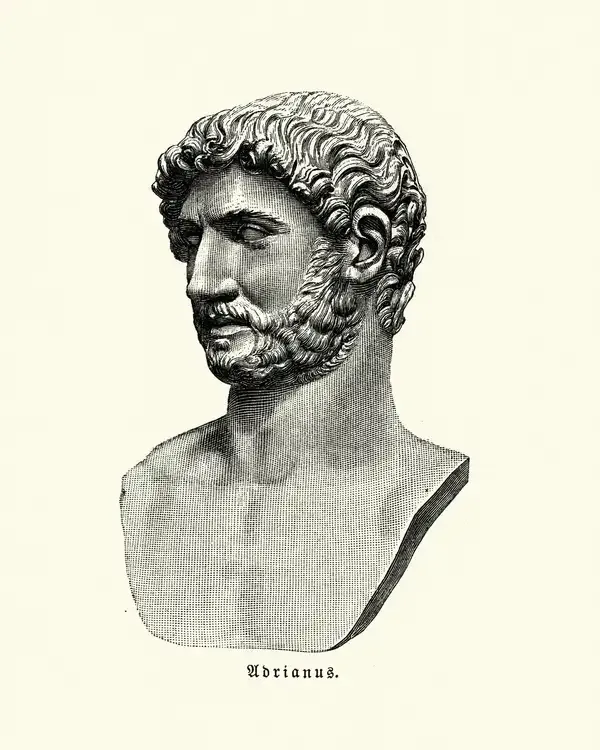
Hadrian, the Roman Emperor from 117 to 138 AD, was deeply influenced by Greek culture, which is evident in his admiration for Greek art, philosophy, and architecture. He was known for his extensive travels throughout the Greek world, revitalizing Athens as a cultural hub and commissioning the construction of the Temple of Olympian Zeus. Hadrian's passion for Greek culture also extended to his personal life, as seen in his relationship with Antinous and his adoption of Greek customs and language, which left a lasting impact on Roman society.

Hadrian, known as one of the Five Good Emperors of Rome, was profoundly influenced by Greek culture, which permeated his policies, architecture, art, and personal philosophies. The Hellenistic world had a significant impact on Roman society, and Hadrian's reign is a prime example of this cultural exchange. Below, we explore the various ways in which Greek culture shaped Hadrian’s life and reign.
Architectural Influence
One of the most significant ways Greek culture influenced Hadrian was through architecture. Hadrian was a great patron of the arts and was known for his ambitious building projects throughout the Roman Empire. His admiration for Greek architecture is evident in several of his constructions:
| Project | Location | Greek Influence |
|---|---|---|
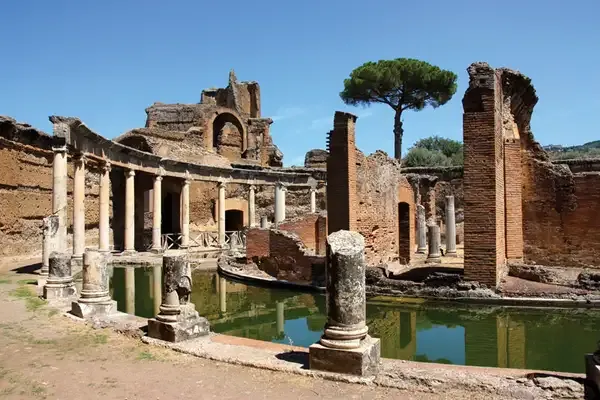
| Hadrian's Villa | Tivoli, Italy | Incorporated Greek architectural styles, including Greek temples and gardens. |
| Temple of Venus and Roma | Rome | Echoed classical Greek temple design, emphasizing symmetry and grandeur. |
| Arch of Hadrian | Athens, Greece | Symbolized the connection between the Greek and Roman worlds. |
Hadrian's Villa, in particular, is a testament to his passion for Greek aesthetics. The villa featured elements borrowed from various Greek styles, reflecting the synthesis of cultures during his reign.
Literary and Philosophical Engagement
Hadrian’s appreciation for Greek culture extended beyond architecture into literature and philosophy. He was an avid reader and a patron of writers, poets, and philosophers, many of whom were influenced by Greek thought.
His correspondence with notable Greek figures, such as the philosopher Epictetus, indicates his profound respect for Greek philosophy, particularly Stoicism. Hadrian embraced the Stoic ideals of virtue, rationality, and self-control, which shaped his approach to governance:
- Virtue: Hadrian aimed to embody the Stoic ideal of moral integrity in his leadership.
- Rationality: He often took a calculated approach to decision-making, influenced by philosophical teachings.
- Self-Control: Hadrian's ability to maintain composure during crises showcased his Stoic influence.
Art and Sculpture
Greek art also had a significant impact on Hadrian’s reign. He was known for his patronage of the arts, promoting Greek sculptors and artists across the empire. Under his rule, there was a revival of classical Greek styles, which can be observed in various sculptures and reliefs from his era.
Hadrian's admiration for Greek art is particularly evident in his use of Greek themes and motifs in public sculptures. For instance, the incorporation of Hellenistic styles in Roman portraits created a unique blend of artistic expression. This fusion not only enhanced the aesthetic appeal of Roman art but also reinforced the cultural prestige of Greece within the Roman Empire.
Religious Syncretism
Hadrian also embraced Greek religion and practices, demonstrating a syncretic approach to spirituality. His support for the Greek pantheon and the worship of Greek deities illustrated his respect for their cultural traditions. Notable actions included:
- Building Temples: Hadrian commissioned temples dedicated to Greek gods, fostering religious integration.
- Encouraging Festivals: He promoted Greek festivals, which celebrated their rich cultural heritage.
This engagement with Greek religion not only honored the cultural practices of the regions within his empire but also solidified his image as a ruler who valued and respected the traditions of his subjects.
Political Philosophy
Hadrian's political philosophy was also significantly shaped by Greek ideas. His governance displayed a blend of Hellenistic ideals and Roman pragmatism. He emphasized the importance of civic duty and participation in government, ideals rooted in Greek democracy.
This approach fostered a sense of loyalty and engagement among Roman citizens, as Hadrian sought to improve the quality of life across the empire through various reforms:
- Legal Reforms: Hadrian implemented legal changes that reflected a more humane and just system, inspired by Greek philosophical ideals.
- Infrastructure Development: His focus on public works, such as roads and aqueducts, was motivated by a desire to improve civic life, a concept rooted in Greek values.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the influence of Greek culture on Hadrian was profound and multifaceted, shaping his architectural projects, literary interests, artistic patronage, religious practices, and political philosophy. Hadrian’s reign not only reflected a deep appreciation for Greek culture but also facilitated a cultural exchange that enriched the Roman Empire. His legacy endures as a testament to the power of cultural integration and the enduring impact of Greek civilization on Rome.